How to Write a Linear Inequality from a Graph?
Writing a linear inequality from a graph involves using a graph of a line to create an inequality that describes all the points that lie either on the line or on one side of the line. A linear inequality is a mathematical statement that compares two expressions using inequality symbols such as "less than," "greater than," "less than or equal to," or "greater than or equal to."

A Step-by-step Guide to Write a Linear Inequality from a Graph
Here are the steps to write a linear inequality from a graph:
Step 1: Identify the slope and \(y\)-intercept of the line
The slope is the steepness of the line, and the \(y\)-intercept is the point where the line crosses the \(y\)-axis.
Step 2: Determine whether the line is solid or dashed
If the line is solid, this means that the points on the line are included in the inequality. If the line is dashed, this means that the points on the line are not included in the inequality. If the line is solid, include the equal sign in the inequality. If the line is dashed, exclude the equal sign.
Step 3: Determine whether the inequality is “greater than” or “less than
If the line slopes upwards from left to right, the inequality is “greater than.” If the line slopes downwards from left to right, the inequality is “less than.”
Step 4: Write the inequality using \(“y”\) for the \(y\)-coordinate and \(“x”\) for the \(x\)-coordinate
If the line is “greater than,” use the “greater than” symbol \((>)\); if the line is “less than,” use the “less than” symbol \((<)\). Use the slope and \(y\)-intercept to write the inequality in slope-intercept form: \(y = mx + b\), where \(“m”\) is the slope and \(“b”\) is the \(y\)-intercept.
Step 5: Write the final inequality
Write the final inequality, using the symbols for “greater than” or “less than” and the values of \(“m”\) and \(“b”\) from the equation.
Writing a Linear Inequality from a Graph – Examples 1
Write the slope-intercept form equation of the following graph.
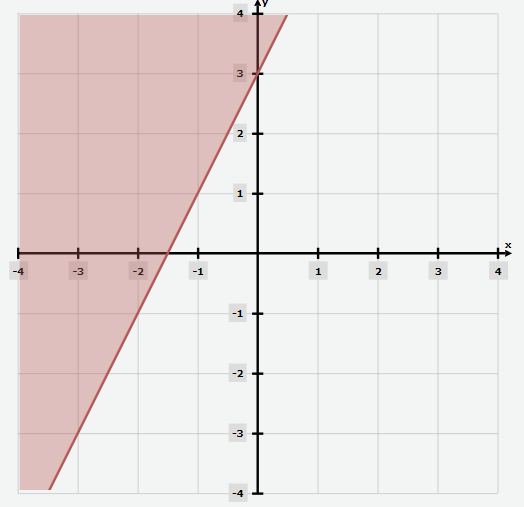
Solution:
To write the inequality equation in slope-intercept form, you should find the \(y\)-intercept \((b)\), and the slope \((m)\), of the solid line. The value of \(b\) is \(3\) because the solid line passes through the \(y\)-axis at \((0,3)\).
Now consider \(2\) points on the solid line to find the slope. You can use \((0,3)\) and \((-2,-1)\):
\(m=\frac{(y_2 – y_1)}{(x_2 – x_1)}=\frac{-1-3}{-2-0}=\frac{-4}{-2}=2→m=2\).
Now use the value of \(b\) and \(m\) and put them into the slope-intercept form formula: \(y=mx+b→y=2x+3\).
Determine the symbol of inequality: you have a solid line and the shaded part is above the line. So, the equation of the inequality is as follows: \(y≥2x+3\).
Exercises for Writing a Linear Inequality from a Graph
Write the slope-intercept form equation of the following graph.
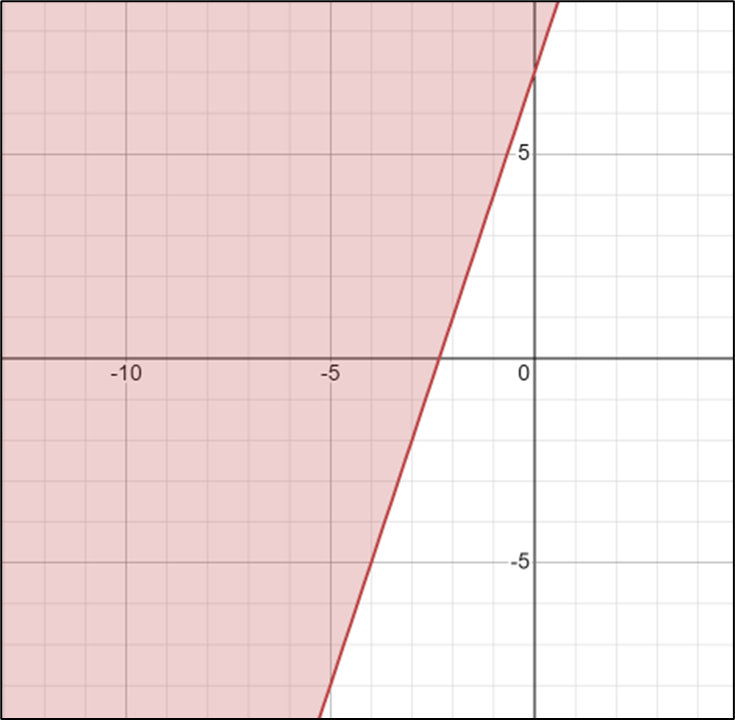
1.
2.
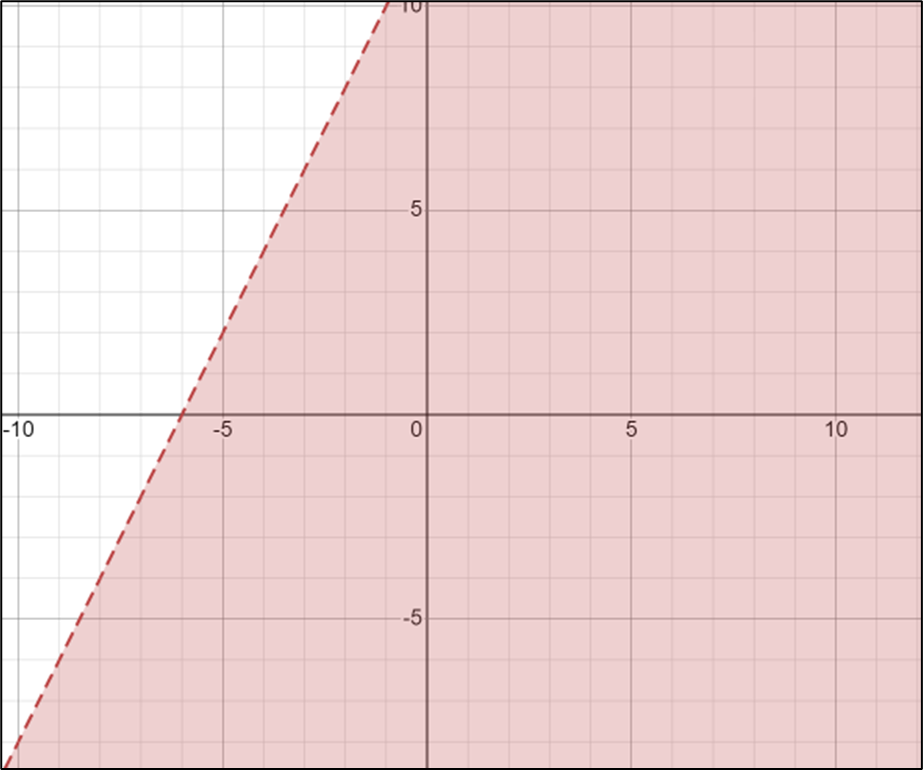
- \(\color{blue}{y≥3x+7}\)
- \(\color{blue}{y<2x+12}\)
Related to This Article
More math articles
- Top 10 6th Grade SBAC Math Practice Questions
- 6th Grade M-STEP Math Worksheets: FREE & Printable
- How to Solve Word Problems Involving Multiplying Mixed Numbers?
- Math Education Trends In Canadian Education System
- The Ultimate SOL Algebra 1 Course (+FREE Worksheets)
- How to Estimate Products of Mixed Numbers
- Top 10 Tips You MUST Know to Retake the ATI TEAS Math
- Solving the Unsolvable: How to Master Systems of Non-linear Equations with Elimination
- The Ultimate ISEE Middle-Level Math Course (+FREE Worksheets & Tests)
- How to Find Standard Deviation
























What people say about "How to Write a Linear Inequality from a Graph? - Effortless Math: We Help Students Learn to LOVE Mathematics"?
No one replied yet.