Order of Operations for 5th Grade: PEMDAS Made Easy
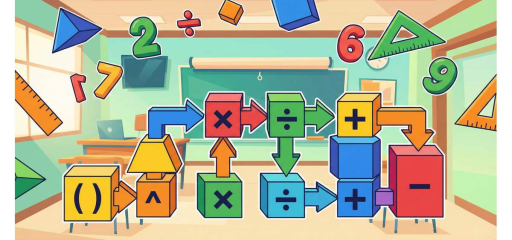
The order of operations is the agreed-upon sequence for evaluating mathematical expressions. Without it, an expression like \(3 + 4 \times 5\) could be interpreted as \((3+4) \times 5 = 35\) or \(3 + (4 \times 5) = 23\)—and we would get different answers. In Grade 5, students use PEMDAS (Parentheses, Exponents, Multiplication and Division, Addition and Subtraction) to ensure everyone evaluates expressions the same way. This skill is essential for algebra, calculator use, and solving multi-step problems.
PEMDAS tells us: first do operations inside parentheses (or other grouping symbols like brackets); then evaluate exponents; then do multiplication and division from left to right; finally do addition and subtraction from left to right. Multiplication and division have equal priority, as do addition and subtraction—we perform them left to right rather than always doing all multiplications before any divisions.
DETAILED EXPLANATION
Order of operations (PEMDAS):
1. P – Parentheses (and brackets, braces): Do operations inside grouping symbols first.
The Absolute Best Book to Ace Grade 5 Math
2. E – Exponents: Evaluate powers (e.g., \(2^3 = 8\)).
3. M & D – Multiplication and Division: From left to right.
4. A & S – Addition and Subtraction: From left to right.
Important: Multiplication and division are done together, left to right. Same for addition and subtraction.
Example: \(3 + 4 \times 5\). No parentheses or exponents. Do multiplication first: \(4 \times 5 = 20\). Then add: \(3 + 20 = 23\).
Example: \(20 – 12 \div 4 + 2\). Division first: \(12 \div 4 = 3\). Then left to right: \(20 – 3 = 17\); \(17 + 2 = 19\).
The Ultimate Middle School Math Bundle: Grades 6–8
WORKED EXAMPLES WITH STEP BY STEP SOLUTIONS
Example 1
Evaluate \(3 + 4 \times 5\)
Solutions:
Step 1: The expression has addition and multiplication. According to PEMDAS, multiplication is done before addition.
Step 2: Compute the multiplication first: \(4 \times 5 = 20\).
Step 3: Then add: \(3 + 20 = 23\).
Step 4: So \(3 + 4 \times 5 = 23\).
Answer: 23
Example 2
Evaluate \((6 + 2) \times 3\)
Mastering Grade 5 Math
Solutions:
Step 1: Parentheses come first. Compute \(6 + 2 = 8\).
Step 2: Replace the parentheses with 8: \(8 \times 3\).
Step 3: Multiply: \(8 \times 3 = 24\).
Step 4: So \((6 + 2) \times 3 = 24\).
Answer: 24
Example 3
Evaluate \(20 – 12 \div 4 + 2\)
Solutions:
Step 1: No parentheses or exponents. Do multiplication and division first, left to right. There is one division: \(12 \div 4 = 3\).
Step 2: Replace: \(20 – 3 + 2\).
Step 3: Do addition and subtraction left to right: \(20 – 3 = 17\); \(17 + 2 = 19\).
Step 4: So \(20 – 12 \div 4 + 2 = 19\).
Answer: 19
Example 4
Evaluate \(2 \times (5 + 3) – 4\)
Solutions:
Step 1: Parentheses first: \(5 + 3 = 8\). Expression becomes \(2 \times 8 – 4\).
Step 2: Multiplication: \(2 \times 8 = 16\). Expression becomes \(16 – 4\).
Step 3: Subtraction: \(16 – 4 = 12\).
Answer: 12
Related to This Article
More math articles
- Decimals Duel: How to Master the Art of Comparison
- TASC Math – Test Day Tips
- How to Classify Polygons: A Step-by-Step Guide to Shape Identification
- Decimals on Display: How to Compare with Number Lines
- Mastering Exponential Growth And Decay: A Comprehensive Guide
- The Math Storyteller: How to Unravel Word Problems of Two-step Equations
- 8th Grade AZMerit Math Worksheets: FREE & Printable
- Bеѕt Cаlсulаtоr fоr ACT Aspire Mаth Tеѕt
- ACT Math Practice Test Questions
- 7th Grade IAR Math Practice Test Questions



























What people say about "Order of Operations for 5th Grade: PEMDAS Made Easy - Effortless Math: We Help Students Learn to LOVE Mathematics"?
No one replied yet.