Opposite Integers

Opposite numbers have the same distance from 0 but they are on the other side of the number lines.
An integer is a number without a decimal or fractional form. This kind of number may be positive, negative, or 0. Opposite integers are considered negative or positive forms of a number.
The only integer that is its opposite is zero. It means the opposite of 0 is 0.
A step-by-step guide to making opposite Integers
Step 1: Identify whether the number is negative or positive.
Step 2: If the number is positive, the opposite side is negative and it is on the left side of zero.
Step 3: If the number is negative, the opposite side is positive and it is on the right side of zero.
Opposite Integers – Examples 1:
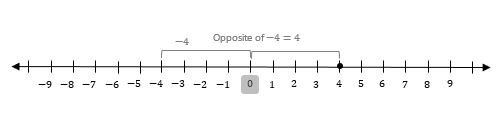
What is the opposite of \(-4\)? Graph it on the number line.
4 is negative so the opposite of \(-4\) will be on the right side of 0. Therefore, the opposite of \(-4\) is 4.
Solutions:
4 is negative so the opposite of \(-4\) will be on the right side of 0. Therefore, the opposite of \(-4\) is 4.
Opposite Integers – Examples 2:
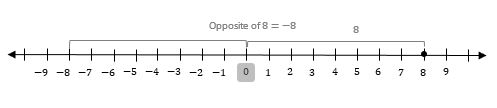
What is the opposite of 8? Graph it on the number line.
Solutions:
8 is positive so the opposite of 8 will be on the left side of 0. Therefore, the opposite of 8 is \(-8\).
Related to This Article
More math articles
- Unlocking the Secrets of Similar Polygons: Shape, Size, and Proportions!
- 6th Grade NHSAS Math Worksheets: FREE & Printable
- The Ultimate PERT Math Formula Cheat Sheet
- How to Use Models to Multiply Two Fractions?
- Product Predictions: How to Estimate Multiplication in Word Problems
- Top 10 Tips to Improve Your Low SAT Math Score
- Journey to the Land of Proportions: How to Write and Solve Equations Utilizing Proportional Relationships
- 7th Grade MCA Math Worksheets: FREE & Printable
- Completing a Table and Make a Graph of Ratios and Rates
- A Comprehensive Look at Average vs Instantaneous Rate of Change




























What people say about "Opposite Integers - Effortless Math: We Help Students Learn to LOVE Mathematics"?
No one replied yet.