Comparing and Ordering Fractions for 5th Grade: Unlike Denominators
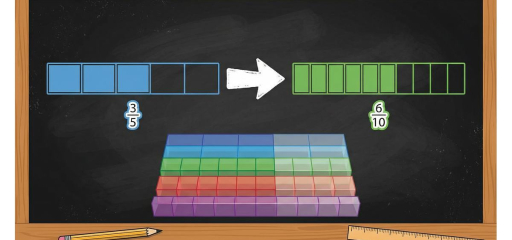
Comparing and ordering fractions helps students decide which fraction is larger, order fractions from least to greatest, and make sense of real-world situations like “who ate more pizza?” or “which measurement is longer?” In Grade 5, students compare fractions with unlike denominators by finding a common denominator (or a common numerator in some cases) or by converting to decimals. The key idea is that we can only compare fractions when they refer to the same whole and the same-size parts—so we need a common denominator to compare “apples to apples.”
To compare \(\frac{2}{3}\) and \(\frac{3}{4}\), we find a common denominator. The LCM of 3 and 4 is 12. \(\frac{2}{3} = \frac{8}{12}\) and \(\frac{3}{4} = \frac{9}{12}\). Since \(\frac{8}{12} < \frac{9}{12}\), we have \(\frac{2}{3} < \frac{3}{4}\). Alternatively, we could convert to decimals: \(\frac{2}{3} \approx 0.667\) and \(\frac{3}{4} = 0.75\), so \(\frac{3}{4}\) is greater.
DETAILED EXPLANATION
Methods to compare fractions:
1. Common denominator: Convert both fractions to equivalent fractions with the same denominator. The fraction with the larger numerator is greater.
The Absolute Best Book to Ace Grade 5 Math
2. Common numerator: In some cases, the fraction with the smaller denominator is greater (e.g., \(\frac{3}{4} > \frac{3}{5}\) because fourths are larger than fifths).
3. Cross-multiply: For \(\frac{a}{b}\) and \(\frac{c}{d}\), compare \(a \times d\) and \(b \times c\). If \(ad > bc\), then \(\frac{a}{b} > \frac{c}{d}\).
4. Decimal conversion: Convert both to decimals and compare.
To order fractions from least to greatest: Find a common denominator, convert all fractions, then order by numerator.
WORKED EXAMPLES WITH STEP BY STEP SOLUTIONS
Example 1
Which is greater: \(\frac{2}{3}\) or \(\frac{3}{4}\)?
Solutions:
The Ultimate Middle School Math Bundle: Grades 6–8
Step 1: Find a common denominator. LCM of 3 and 4 is 12.
Step 2: Convert: \(\frac{2}{3} = \frac{2 \times 4}{3 \times 4} = \frac{8}{12}\); \(\frac{3}{4} = \frac{3 \times 3}{4 \times 3} = \frac{9}{12}\).
Step 3: Compare numerators: 8 < 9, so \(\frac{8}{12} < \frac{9}{12}\).
Step 4: Therefore \(\frac{2}{3} < \frac{3}{4}\). \(\frac{3}{4}\) is greater.
Answer: \(\frac{3}{4}\) is greater.
Example 2
Order from least to greatest: \(\frac{1}{2}\), \(\frac{2}{5}\), \(\frac{3}{10}\)
Solutions:
Step 1: LCM of 2, 5, 10 = 10. Convert: \(\frac{1}{2} = \frac{5}{10}\); \(\frac{2}{5} = \frac{4}{10}\); \(\frac{3}{10} = \frac{3}{10}\).
Mastering Grade 5 Math
Step 2: Order by numerator: \(\frac{3}{10} < \frac{4}{10} < \frac{5}{10}\).
Step 3: In original form: \(\frac{3}{10}\), \(\frac{2}{5}\), \(\frac{1}{2}\).
Answer: \(\frac{3}{10}\), \(\frac{2}{5}\), \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Example 3
Sam ate \(\frac{2}{5}\) of a pizza and Mia ate \(\frac{1}{2}\). Who ate more?
Solutions:
Step 1: Compare \(\frac{2}{5}\) and \(\frac{1}{2}\). Common denominator: 10. \(\frac{2}{5} = \frac{4}{10}\); \(\frac{1}{2} = \frac{5}{10}\).
Step 2: \(\frac{5}{10} > \frac{4}{10}\), so \(\frac{1}{2} > \frac{2}{5}\).
Step 3: Mia ate more.
Answer: Mia ate more.
Example 4
Which is greater: \(\frac{4}{7}\) or \(\frac{5}{9}\)?
Solutions:
Step 1: Common denominator: LCM of 7 and 9 = 63. \(\frac{4}{7} = \frac{36}{63}\); \(\frac{5}{9} = \frac{35}{63}\).
Step 2: 36 > 35, so \(\frac{36}{63} > \frac{35}{63}\).
Answer: \(\frac{4}{7}\) is greater.
Related to This Article
More math articles
- Full-Length 7th Grade Common Core Math Practice Test-Answers and Explanations
- How to Solve Multi-step Word Problems for Finding Starting and Ending Times
- Subtracting Multi-Digit Numbers for 4th Grade
- Reading and Writing Numbers for 5th Grade: Standard, Word, and Expanded Form
- Balancing Math Assignments and Academic Papers: Tips for Busy Students
- ASVAB Math FREE Sample Practice Questions
- How to Factor and Simplify Trigonometric Expressions
- How to Navigate the Fraction Jungle: A Guide to Adding Fractions with Unlike Denominators
- FREE 6th Grade STAAR Math Practice Test
- The Ultimate GACE Elementary Education Math Course



























What people say about "Comparing and Ordering Fractions for 5th Grade: Unlike Denominators - Effortless Math: We Help Students Learn to LOVE Mathematics"?
No one replied yet.